Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis: USMLE Immunology
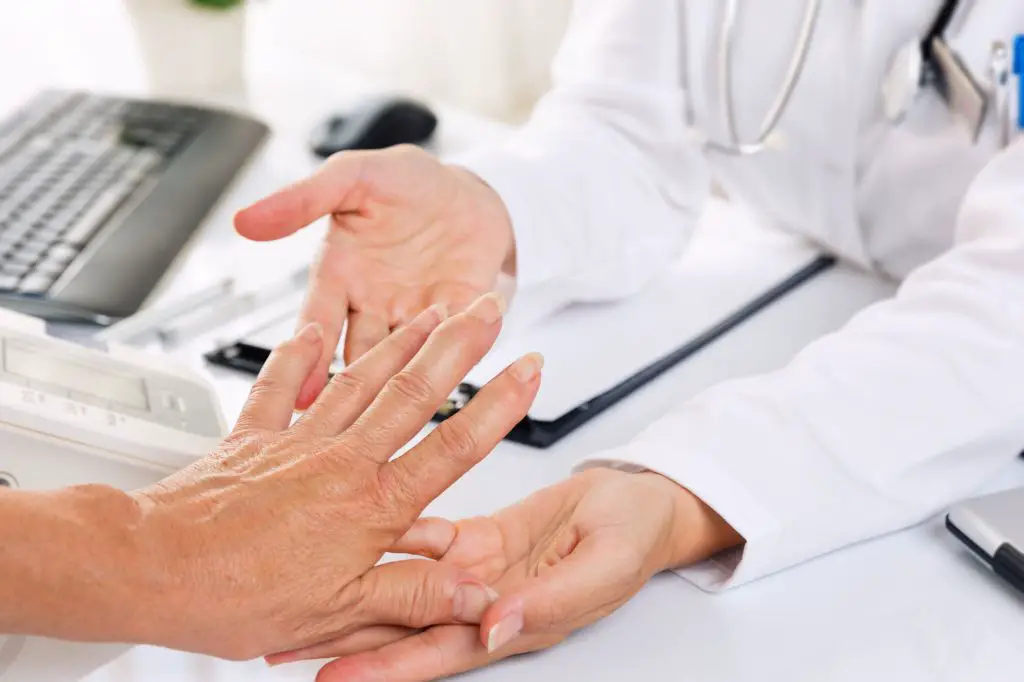
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation in the joints of hands, feet, knees, etc. In this quick and easy lesson, we explain the standard medical treatment for patients with rheumatoid arthritis at the USMLE immunology level, including DMARDS (synthetics and biologics), NSAIDS, and glucocorticoids.

NSAIDS Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis: USMLE
NSAIDS stand for non-steroidal anti-inflammatories. They are medications, such as ibuprofen, that reduce inflammation for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. However, NSAIDS do not affect the progress of the disease. These only help reduce inflammation.
Glucocorticoids or Corticosteroids Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis: USMLE
Glucocorticoids , also known as corticosteroids, are common treatment for rheumatoid arthritis as well by reducing both inflammation and pain in patients. Unlike NSAIDS, glucocorticoids reduce both inflammation and pain, but similar to NSAIDS, glucocorticoids do not slow down the progress of rheumatoid arthritis.

DMARDs Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs for Rheumatic Arthritis: USMLE
DMARDs also known as disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs slow down and delay the progress the rheumatic arthritis. DMARDs for rheumatic arthritis consist of 2 main classes including 1) Synthetics and 2) Biologics.
Synthetic DMARDs for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Synthetic DMARDs include methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, and leflunomide, to name a few. Methotrexate is a very important DMARD drug to know for Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment because Methotrexate is the 1st Choice Drug for treatment. Methotrexate suppresses inflammation, pain, and disease progression.
Biologics or biologicals in DMARD treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis include different types that target specific factors of the immune system. In general, there are TNF-alpha inhibitors, B-cell inhibitors, T-cell inhibitors, IL-6 Inhibitor, and IL-1 inhibitors.
Abatacept –| T-cells or specifically inhibits T-cell activation
Rituximab –| B-cells
Adalimumab (Humira), etanercept, infliximab, golimumab, and cortolizumab –| TNF-alpha or Tumor necrosis factor
Anakinra –| IL-1 receptor, and usually co-administered with methotrexate
Tocilizumab –| IL-6

Click and check out these popular articles for more information: 🙂
Ectoderm vs Endoderm vs Mesoderm
Circulatory System: Blood Flow Pathway Through the Heart
Circulatory System: Heart Structures and Functions
Ductus Arteriosus Vs Ductus Venosus Vs Foramen Ovale: Fetal Heart Circulation
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Definition, Types, Symptoms, and Prevention
Upper Vs Lower Respiratory System: Upper vs Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Seven General Functions of the Respiratory System
Digestive System Anatomy: Diagram, Organs, Structures, and Functions
Kidney Embryology & Development: Easy Lesson
Psychology 101: Crowd Psychology and The Theory of Gustave Le Bon
Introduction to Evolution: Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace
Copyright © 2022 Moosmosis Organization: All Rights Reserved
All rights reserved. This essay or any portion thereof may not be reproduced or used in any manner whatsoever
without the express written permission of the publisher.
Categories: anatomy, Biology, cell biology, education, health, immunology, medicine, stem













Excellent essay on arthritis and treatments! Arthritis is becoming more common these days
LikeLiked by 2 people
Great arthritis. My gran gran had arthritis.
LikeLiked by 2 people
superbly written
LikeLiked by 2 people
Excellent medical article!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Excellent article! It’s so helpful. Now I know whether I need to go to urgent care or the hospital. Thanks!
LikeLiked by 2 people