What is Wilson disease? Do not fret, young medical student. In this lesson, we learn about Wilson disease and include high-yield medical school information, such as causes, pathology, diagnosis, and treatments. Test yourself with our high-yield question vignettes with answers on Wilson Disease.
What is Wilson disease?
Wilson disease is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by impaired biliary copper secretion, leading to copper deposition in the liver, brain, eyes, and other tissues.
Wilson disease usually presents in patients < 30 years of age.
Wilson Disease: Mutation and Pathology
Wilson disease is caused by a mutation of the ATP7B, leading to 3 main causes:
- Decreased copper secretion into bile
- Decreased copper incorporation into ceruloplasmin
- Decreased ceruloplasmin secretion into blood
ATP7B encodes a transmembrane copper transporter. The defect is linked to chromosome 13.

COPPER = Chromosome 13 = ATP7B mutation = WILSON’s DISEASE
Wilson Disease: Physical Exam
Physical exam findings in a patient with Wilson disease may include:
- Kayser-Fleischer rings in the cornea (pathognomonic)
- Hepatomegaly
- Parkinsonian tremor
Slit-lamp examination of patients with Wilson disease classically reveals Kayser-Fleischer rings, which are green/brown deposits of copper in the Descemet membrane of the cornea.
Patients with Wilson disease often present with movement disorders that resemble Parkinson disease due to copper deposition in the basal ganglia, in particular the putamen. Copper deposition in other parts of the CNS can cause dementia, dyskinesia, and dysarthria.
High Yield: Copper deposits in the basal ganglia for patients with Wilson disease.
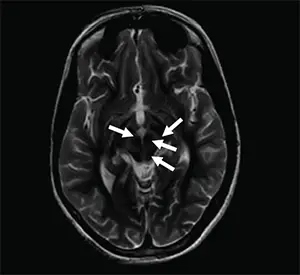
Basal Ganglia = Parkinson symptoms
Liver symptoms may include:
- Asterixis
- Jaundice
- Mental status changes (secondary to hepatic encephalopathy)
- Acute hepatitis
- Portal hypertension
Wilson Disease: Laboratory Findings & Diagnosis
Coombs-negative hemolytic anemia can occur in Wilson disease since copper is toxic to red blood cell membranes.
Copper deposition in the joints causes degenerative arthritis, typically affecting the spine and large joints.
Wilson disease is diagnosed in the following ways:
- Neurologic symptoms + Kayser-Fleischer rings + ceruloplasmin <20 mg/dL
OR
- Isolated liver disease + hepatic copper concentration >250 mcg/g dry weight liver + low serum ceruloplasmin
If neurologic symptoms and Keyser-Fleischer rings are absent, liver biopsy and quantitative copper determination is necessary for diagnosis.
Genetic testing is not required for diagnosis. Genetic studies are useful for screening family members of affected patients in whom there has been a previously identified mutation.
Patients with Wilson’s disease will have decreased serum ceruloplasmin with elevated free copper but decreased total copper.

Wilson Disease: Treatment
Complications of Wilson disease include:
- Cirrhosis
- Liver failure
- Persistent neurological deficits (Parkinsonian symptoms, dementia)
- Psychiatric problems (personality changes, depression, bipolar disorder, psychosis)
- Amino aciduria
- Nephrocalcinosis
Therefore, it is important to treat Wilson disease early.
Copper chelating agents such as D-penicillamine or trientine are the preferred treatment for patients with Wilson disease who are not experiencing acute liver failure.
Oral zinc preparations (e.g. zinc acetate, zinc gluconate) interfere with copper absorption and can be used in patients who do not tolerate chelating agents.

High Yield Mnemonic: Zinc ==== | blocks Copper absorption
D-penicillamine /Trientine = pencils attaching to copper = CHELATES copper
Mechanism: Zinc induces metallothionein, a metal chelator expressed in enterocytes. Since metallothionein has a greater affinity for copper than for zinc, copper is preferentially sequestered within enterocytes, thereby impairing release to the circulation. The chelated copper is ultimately excreted as part of normal enterocyte turnover.
Penicillamine can chelate heavy metals such as copper, lead, and mercury and form a soluble complex that is renally excreted in the urine.
Medications used to treat the other symptoms of Wilson disease include:
- Anticholinergics, GABA antagonists, and levodopa (for treatment of parkinsonism)
- Antiepileptics (to treat seizures)
- Neuroleptics (to treat psychosis and other psychiatric symptoms)
- Lactulose (to treat hepatic encephalopathy)
Orthotopic liver transplantation is curative for Wilson disease and may be indicated in the case of worsening hepatic function or progression of disease.

Check out these popular articles 🙂
Circulatory System: Blood Flow Pathway Through the Heart
Ectoderm vs Endoderm vs Mesoderm
Circulatory System: Heart Structures and Functions
Ductus Arteriosus Vs Ductus Venosus Vs Foramen Ovale: Fetal Heart Circulation
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Definition, Types, Symptoms, and Prevention
Upper Vs Lower Respiratory System: Upper vs Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Seven General Functions of the Respiratory System
Digestive System Anatomy: Diagram, Organs, Structures, and Functions
Kidney Embryology & Development: Easy Lesson
Autocrine vs Paracrine vs Endocrine: What are the Differences?
Their Eyes Were Watching God: Mule Symbol
Shoulder Abduction Muscles: Medical Anatomy and USMLE
Cell Membrane Dynamics: Flippase vs Floppase vs Scramblase
Cell Membrane Fluidity: Factors That Influence and Increase the Cell Membrane Fluidity
Psychology 101: Crowd Psychology and The Theory of Gustave Le Bon
Introduction to Evolution: Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace
An Overview of Shorthand: History and Types of Shorthand
Calculus: Two Important Theorems – The Squeeze Theorem and Intermediate Value Theorem
Copyright © 2023 Moosmosis Organization: All Rights Reserved
All rights reserved. This essay first published on moosmosis.org or any portion thereof may not be reproduced or used in any manner whatsoever
without the express written permission of the publisher at moosmosis.org.

Please Like, Share, and Subscribe to our Email List at moosmosis.org, Facebook, Twitter, Youtube to support our open-access youth education initiatives! 🙂
Categories: anatomy, Biology, cell biology, chemistry, health, immunology, medicine, stem













Amazing article! These are excellent articles and fun to learn about.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you very much! Glad they are fun. Have an amazing day!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Fascinating!!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you very much!! Have an amazing day!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Wonderful information about Wilson Disease.
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thank you so much, Alex! Have a wonderful day!
LikeLike
Interesting facts about Wilson’s disease!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thank you kind soul! Happy learning!! 🙂
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you so much!!
LikeLiked by 1 person
NICE POST ❤️💖💗
Blessed and happy afternoon 🌞
Greetings 👋🇪🇸
Together we grow if we help each other 💕🙏
🌹🌷🌻🏵️🌺🪷
David López Moncada PK 🌎
LikeLiked by 1 person
Happy New Year and thank you so much David! 🌹🌷🌻🏵️🌺 You have a nice website too! ❤️💖💗Have a blessed and happy afternoon too! 🌞 💕🙏
LikeLiked by 1 person