Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) are two chronic liver diseases that affect the bile ducts, which are responsible for carrying bile from the liver to the small intestine. While they have some similarities, they are distinct conditions with different causes and treatments. In this quick lesson, we will review the differences and similarities of primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PBC) vs (PSC). Stay tuned for practice multiple choice questions and answers at the end!
Primary Biliary Cholangitis vs Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Similarities and Differences
Introduction: PBC vs PSC
PBC is a autoimmune disorder that occurs when the body’s immune system attacks and damages the small bile ducts in the liver. This leads to scarring and inflammation of the ducts, which can eventually result in liver damage and cirrhosis. PBC is more common in women, and the risk increases with age. Symptoms of PBC may include fatigue, itching, and yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice).
PSC, on the other hand, is a progressive disease that results from inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts. It can occur in both men and women, and is more common in people with inflammatory bowel disease such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. PSC can also cause jaundice and itching, as well as abdominal pain and weight loss.
PBC vs PSC: Pathology and Treatment
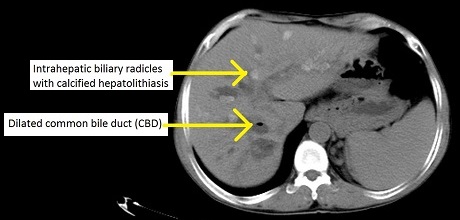
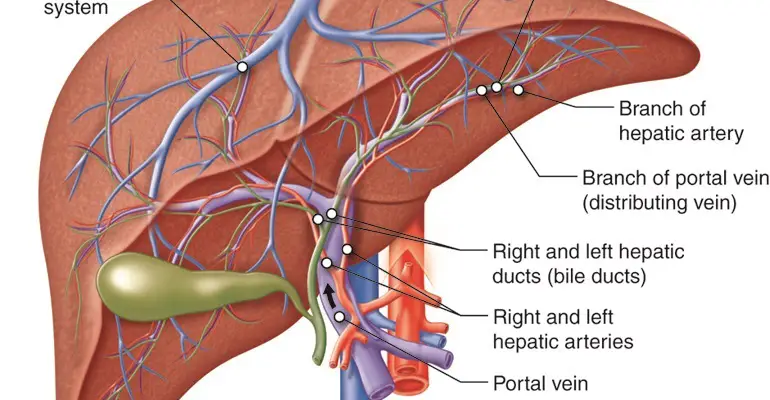
One of the main differences between PBC and PSC is the cause of the bile duct damage. PBC is an autoimmune disorder, while PSC is caused by inflammation and scarring. This means that the treatments for these conditions may be different. PSC is characterized by damage of medium to large extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts, whereas PBC chiefly targets small intrahepatic bile ducts (Park et al. 2022).
PBC is often treated with medications that suppress the immune system, such as ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) or immunosuppressants. These medications can help slow down the progression of the disease and may improve symptoms. In some cases, a liver transplant may be necessary if the liver has been severely damaged.
PSC, on the other hand, is more difficult to treat and there is no cure for the condition. Treatment may include medications to manage symptoms and prevent complications, such as antibiotics to prevent infections or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to control abdominal pain. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
PBC vs PSC: Prognosis
Another difference between PBC and PSC is the prognosis. PBC is generally a slower progressing disease, and many people with PBC can live for many years with the condition. However, PSC is a more aggressive disease and can lead to liver failure and death in a shorter period of time.

There are also some notable differences in the prevalence and risk factors for these conditions. PBC is more common in women and tends to occur in people over the age of 40. PSC, on the other hand, can occur at any age and is more common in men. Risk factors for PSC include a history of inflammatory bowel disease and smoking.
In conclusion, primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis are two chronic liver diseases that affect the bile ducts. While they have some similarities, they are distinct conditions with different causes and treatments. PBC is an autoimmune disorder that is treated with medications that suppress the immune system, while PSC is caused by inflammation and scarring and is more difficult to treat. PBC is generally a slower progressing disease, while PSC is more aggressive and can lead to liver failure and death in a shorter period of time.
Summary Table: PBC vs PSC
| Feature | PBC (Primary Biliary Cirrhosis) | PSC (Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis) |
|---|---|---|
| Risk factors | Female gender, autoimmune disorders | Inflammatory bowel disease, history of appendectomy/inflammatory bowel disease |
| Patient Population | Female gender, over age 40 | Any age, more common in men; more likely to have a IBD history such as ulcerative colitis |
| Symptoms | Fatigue, itching, jaundice Progressive jaundice, hepatomegaly, cirrhosis Skin manifestations including xanthomas | Fatigue, itching, jaundice, abdominal pain |
| Laboratory Findings | Antimitochondrial antibody High cholesterol levels High Alk phosphatase and High aminotransferase | Beads on a string appearance on imaging (indicative of dilation and stricture of bile duct) High aminotransferases (but typically <300) |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, liver biopsy | Blood tests, liver biopsy, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) |
| Treatment | Ursodeoxycholic acid, immunosuppressants | NSAIDs, immunosuppressants, liver transplant |
| Prognosis | Progressive liver damage, potential for cirrhosis and liver cancer | Progressive liver damage, potential for cirrhosis and liver cancer |
Practice Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
Question 1: Which of the following is true about PBC and PSC?
A) Both diseases primarily affect the heart.
B) Both diseases are caused by bacterial infections.
C) PBC is an autoimmune disease, while PSC is not.
D) PSC is an autoimmune disease, while PBC is not.
Answer: D) PSC is an autoimmune disease, while PBC is not. Explanation: PSC is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, while PBC is also an autoimmune disease characterized by the destruction of small bile ducts.
Question 2: Which organ is primarily affected by PBC and PSC?
A) Kidneys
B) Lungs
C) Liver
D) Pancreas
Answer: C) Liver Explanation: Both PBC and PSC primarily affect the liver and the bile ducts within it.
Question 3: Which symptom is more commonly associated with PBC than with PSC?
A) Jaundice
B) Itchy skin
C) Abdominal pain
D) Joint pain
Answer: B) Itchy skin Explanation: Pruritus (itchy skin) is a common symptom of PBC due to the accumulation of bile salts, whereas it is less commonly associated with PSC.
Question 4: What is the main treatment for end-stage liver disease caused by PBC or PSC?
A) Antibiotics
B) Chemotherapy
C) Liver transplantation
D) Radiation therapy
Answer: C) Liver transplantation Explanation: Liver transplantation is the main treatment option for end-stage liver disease resulting from both PBC and PSC.
Question 5: Which diagnostic test is commonly used to assess the severity of liver damage in PBC and PSC?
A) Electrocardiogram (ECG)
B) Liver biopsy
C) Urinalysis
D) Blood glucose test
Answer: B) Liver biopsy Explanation: A liver biopsy is often performed to assess the degree of liver damage and inflammation in both PBC and PSC.
Question 6: Which of the following inflammatory bowel diseases is commonly associated with PSC?
A) Crohn’s disease
B) Ulcerative colitis
C) Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
D) Celiac disease
Answer: B) Ulcerative colitis Explanation: PSC is frequently associated with ulcerative colitis, an inflammatory bowel disease, which is not commonly seen in conjunction with PBC.
Question 7: Which liver function test result is typically elevated in both PBC and PSC?
A) Alanine transaminase (ALT)
B) Creatine kinase (CK)
C) Serum bilirubin
D) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Answer: C) Serum bilirubin Explanation: Elevated serum bilirubin levels are indicative of liver dysfunction and can be observed in both PBC and PSC.
Question 8: Which demographic group is more commonly affected by PBC and PSC?
A) Children under 10 years old
B) Adolescents and young adults
C) Middle-aged adults
D) Elderly individuals over 90 years old
Answer: C) Middle-aged adults Explanation: Both PBC and PSC are more commonly diagnosed in middle-aged adults, typically between 30 and 60 years of age.
Question 9: Which disease has a stronger association with the development of liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma)?
A) PBC
B) PSC
C) Both PBC and PSC
D) Neither PBC nor PSC
Answer: B) PSC Explanation: PSC has a stronger association with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma compared to PBC.
Question 10: Which disease is characterized by progressive destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts?
A) PBC
B) PSC
C) Both PBC and PSC
D) Neither PBC nor PSC
Answer: A) PBC Explanation: PBC is characterized by the progressive destruction of the intrahepatic (inside the liver) bile ducts due to an autoimmune process, whereas PSC involves inflammation and scarring of both intrahepatic and extrahepatic (outside the liver) bile ducts.
Check out these popular articles 🙂
Circulatory System: Blood Flow Pathway Through the Heart
Ectoderm vs Endoderm vs Mesoderm
Circulatory System: Heart Structures and Functions
Ductus Arteriosus Vs Ductus Venosus Vs Foramen Ovale: Fetal Heart Circulation
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Definition, Types, Symptoms, and Prevention
Upper Vs Lower Respiratory System: Upper vs Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Seven General Functions of the Respiratory System
Digestive System Anatomy: Diagram, Organs, Structures, and Functions
Kidney Embryology & Development: Easy Lesson
Autocrine vs Paracrine vs Endocrine: What are the Differences?
Their Eyes Were Watching God: Mule Symbol
Shoulder Abduction Muscles: Medical Anatomy and USMLE
Cell Membrane Dynamics: Flippase vs Floppase vs Scramblase
Cell Membrane Fluidity: Factors That Influence and Increase the Cell Membrane Fluidity
Psychology 101: Crowd Psychology and The Theory of Gustave Le Bon
Introduction to Evolution: Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace
An Overview of Shorthand: History and Types of Shorthand
Calculus: Two Important Theorems – The Squeeze Theorem and Intermediate Value Theorem
What is the Cori Cycle? Quick and Easy Explanation: MCAT and USMLE
Copyright © 2023 Moosmosis Organization: All Rights Reserved
All rights reserved. This essay first published on moosmosis.org or any portion thereof may not be reproduced or used in any manner whatsoever
without the express written permission of the publisher at moosmosis.org.

Please Like, Share, and Subscribe to our Email List at moosmosis.org, Facebook, Twitter, Youtube to support our open-access youth education initiatives! 🙂











Excellent article on PSC v PBC! I’ve learned something new today.
LikeLiked by 1 person
Fantastic comparison of the two! One of my aunts had primary biliary cholangitis. Superb analysis!
LikeLiked by 1 person
phenomenal essay!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Thank you, Dr. Keys! 😀
LikeLiked by 1 person
You’re very welcome Moosmosis!! 😀
LikeLiked by 2 people