
Biology Unit 3 Study Guide: Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Check out:
Biology Study Guide Book just published and on sale! : Study Guides: Biology Unit Review Practice Questions and Answers
Biology Unit 1 Study Guide: Ecology and Scientific Method
Biology Unit 2 Study Guide: Basic Building Blocks of Life
BIOLOGY UNIT 3 STUDY GUIDE: CELL ENERGY – PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Study Guide: Genetics, MeisosiS, DNA, and Protein Synthesis
BioLogy Unit 5 Study Guide: EVOLUTION
All living things obtain and use energy…
How do plants convert energy from the sun into food for energy?
Trace the path of energy from the sun to glucose.
Sun –> Energy is captured in leaves by chlorophyll inside the organelle chloroplasts. –> Energy is captured by electrons and carried in ATP and NADPH. –> The high-energy electrons are used to build molecules the cell need like glucose.
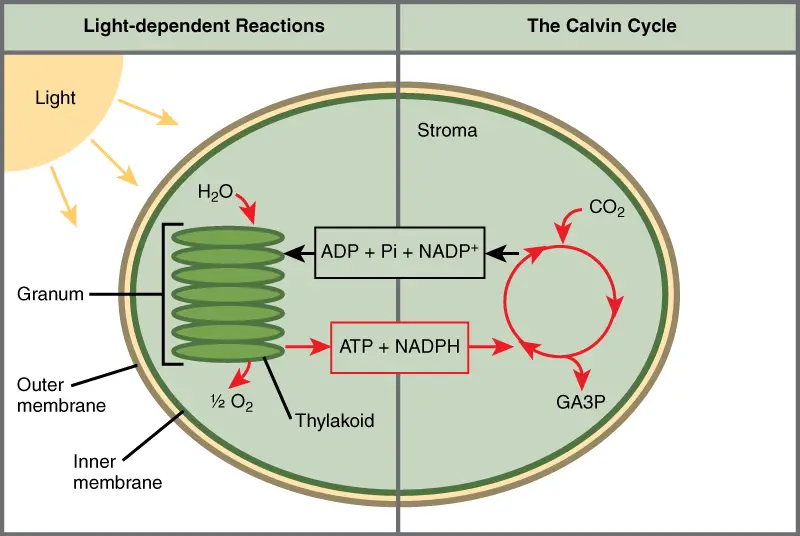
What do plants need in order to undergo photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis within chloroplasts is divided into two phases:
1) Light Reactions (occurs in the thylakoid disk)
i) Electrons excited by the sun are carried by ATP and NADPH to where the next phase occurs. ii) (a) H2O breaks apart to replace the missing electron from the chlorophyll. This is called photolysis and releases (b) oxygen into the air.
2) Calvin Cycle (occurs in the stroma)
i) Using energy from the electrons, molecule of (c) CO2 join together to form (d) glucose.
Complete the equation for photosynthesis using the exercise above:
sunlight + (a) H2O + (c) CO2 –> (b) oxygen + (d) glucose
Check out:
Biology Study Guide Book just published and on sale! : Study Guides: Biology Unit Review Practice Questions and Answers
Biology Unit 1 Study Guide: Ecology and Scientific Method
Biology Unit 2 Study Guide: Basic Building Blocks of Life
BIOLOGY UNIT 3 STUDY GUIDE: CELL ENERGY – PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Study Guide: Genetics, MeisosiS, DNA, and Protein Synthesis
BioLogy Unit 5 Study Guide: EVOLUTION
How do the reactants get to the chloroplasts inside a plant?
- Most SUNLIGHT is captured by chloroplasts found in the C) palisade mesophyll.
- WATER gets into the leaf through the xylem, NOT through A) epidermis because of the water-proof B) cuticle.
- CARBON DIOXIDE enters the leaf through the F) stomata, which also allows water and oxygen to leave the leaf. This opening is controlled by E) guard cells. When there is little water available, it is usually closed to conserve water.

How is energy released from glucose into a form of energy the cell can use?
Cells need to get energy in the form of ATP in order to use it. The conversion of food (glucose) into ATP occurs in the organelle mitochondria. This process is CELLULAR RESPIRATION.
Trace the path of energy from glucose to ATP.
Glucose contains energy. –> Glucose is broken down into smaller molecules and energy is captured by ATP and electron carriers NADH and FADH2. –> Electron carriers drop off high-energy electrons to produce usable energy in the form of ATP.
The energy found in ATP is released when the bond between 2nd and 3rd phosphate is broken.
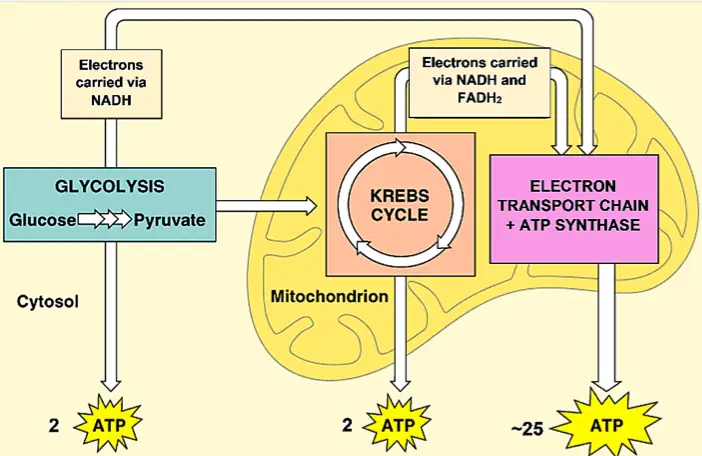
What do plants AND animals need to undergo cellular respiration?
Cellular Respiration is divided into three phases:
1) glycolysis
i) (a) glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid so it can pass into the mitochondria. ii) 2 ATP created
2) Krebs cycle
i) Energy is captured by ATP and electron carriers high-energy electrons electron transport chain NADH and FADH2.
ii) (b) CO2 is released as by-product.
3) Electron Transport Chain
i) Electron carriers drop off high energy electrons which are passed down to (c) oxygen, the final electron acceptor.
ii)(c) oxygen joins with H+ to form (d) water.
iii) LOTS of (e)ATP are made.
Complete the equation for cellular respiration using the exercise above:
(a)C6H12O6 + (c)O2 –> (b)CO2 + (d) H2O + (e)energy in the form of ATP

Check out:
Biology Study Guide Book just published and on sale! : Study Guides: Biology Unit Review Practice Questions and Answers
Biology Unit 1 Study Guide: Ecology and Scientific Method
Biology Unit 2 Study Guide: Basic Building Blocks of Life
BIOLOGY UNIT 3 STUDY GUIDE: CELL ENERGY – PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Study Guide: Genetics, MeisosiS, DNA, and Protein Synthesis
BioLogy Unit 5 Study Guide: EVOLUTION
What happens when oxygen is not available for cellular respiration?
If oxygen is not available, then the electron carriers NADH and FADH2 are unable to release their electrons and pick up more. When this happens, the process of the
Kreb cycle and electron transport chain cannot make ATP.
In order to continue making ATP without oxygen, some cells can switch to a process called fermentation. This relies on glycolysis to make ATP. Yeast and bacteria will then convert pyruvic acid to ethanol and CO2 while muscle cells in animals will convert it into lactic acid in order to regenerate NAD+.
Subscribe, share, and stay tuned for the study guide book coming soon!
Check out:
Biology Study Guide Book just published and on sale! : Study Guides: Biology Unit Review Practice Questions and Answers
Biology Unit 1 Study Guide: Ecology and Scientific Method
Biology Unit 2 Study Guide: Basic Building Blocks of Life
BIOLOGY UNIT 3 STUDY GUIDE: CELL ENERGY – PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND CELLULAR RESPIRATION
BIOLOGY UNIT 4 Study Guide: Genetics, MeisosiS, DNA, and Protein Synthesis
BioLogy Unit 5 Study Guide: EVOLUTION
Thanks for reading, and have a wonderful day!
Click and check out these popular articles for more information: 🙂
Ectoderm vs Endoderm vs Mesoderm
Circulatory System: Blood Flow Pathway Through the Heart
Circulatory System: Heart Structures and Functions
Ductus Arteriosus Vs Ductus Venosus Vs Foramen Ovale: Fetal Heart Circulation
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Definition, Types, Symptoms, and Prevention
Upper Vs Lower Respiratory System: Upper vs Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Seven General Functions of the Respiratory System
Digestive System Anatomy: Diagram, Organs, Structures, and Functions
Kidney Embryology & Development: Easy Lesson
Psychology 101: Crowd Psychology and The Theory of Gustave Le Bon
Introduction to Evolution: Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace

Please Like and Subscribe to our Email List at moosmosis.org, Facebook, Twitter, Youtube to support our open-access youth education initiatives! 🙂












Excellent biology study guides! Thanks for sharing
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you! Happy to share!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Exceptional articles on biology!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you!!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Wonderful, comprehensive study guide!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you —you’re wonderful!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Excellent and very helpful article on biology especially photosynthesis vs cellular respiration!
LikeLiked by 2 people
Reblogged this on Nutrition 101.
LikeLike