Direct vs Indirect Hernia: What is the difference between direct and indirect inguinal hernias?
In this easy-to-understand lesson, we explore the differences between direct inguinal hernias and indirect inguinal hernias. Overall, an inguinal hernia is a medical condition, where protrusion or bulge of abdominal contents into the groin area and/or inguinal canal. There are two types of inguinal hernias: 1) direct inguinal hernia and 2) indirect inguinal hernia.
Are direct or indirect hernias more common?
What are the anatomical borders of Hasselbach’s Triangle?
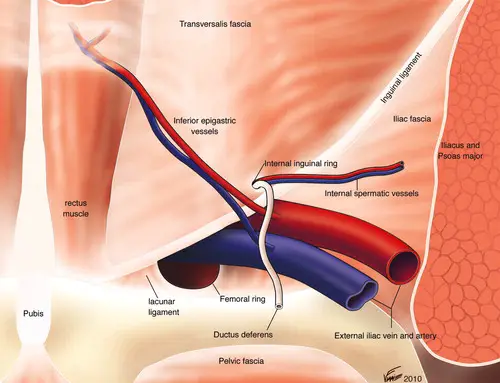
The borders of the Hasselbach’s Triangle are the following:
- Inferior epigastric vessels
- Inguinal ligament
- Lateral border of the rectus abdominis
| Direct Inguinal Hernia | Indirect Inguinal Hernia |
| Medical to epigastric vessels | Lateral to epigastric vessels |
| Cause: Abdomen strain/muscle weakness | Cause: Problems with processus vaginalis descent for baby boys |
| Acquired | Usually inherited |
| Location: Hasselbach’s Triangle and directly behind superficial inguinal ring | Location: Coming out from Deep Inguinal Ring, descending to scrotum |
| Rarely in scrotum | Can pass into scrotum |
| Common in elderly men with weak abdominal muscles | Common in men > females, because usually congenital |
Both types of inguinal hernias, both direct and indirect hernias, are more common in males than females.
Indirect hernias are more common than direct hernias in males.
Femoral hernias are more common in females than males.

Indirect Hernia Mnemonic: Indirect Hernias are IN deeeeeeppp. Indirect = Deep inguinal canal
Superficial Inguinal Ring = Where External Oblique Muscle is
Deep Inguinal Ring = Where Transversus Abdominis Muscle is
Development of Inguinal Canal
Gonads, testes or ovaries, descend through the abdominal wall cavity. The gubernaculum ligament guides gonads down, forming along with it the processus vaginalis structure that surrounds the gonad like a sac. The processus vaginalis usually degenerates later, but if it does not, this could lead to an indirect inguinal hernias. The gubernaculum over time during development becomes shorter and turns into the short scrotal ligament that tethers the balls to the scrotal sac. For females, the gubernaculum ligament becomes the ovarian ligament that attaches the ovaries to the ligament and the round ligament of the uterus.
Click and check out these popular articles for more information: 🙂
Ectoderm vs Endoderm vs Mesoderm
Circulatory System: Blood Flow Pathway Through the Heart
Circulatory System: Heart Structures and Functions
Ductus Arteriosus Vs Ductus Venosus Vs Foramen Ovale: Fetal Heart Circulation
Cardiac Arrhythmias: Definition, Types, Symptoms, and Prevention
Upper Vs Lower Respiratory System: Upper vs Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Seven General Functions of the Respiratory System
Digestive System Anatomy: Diagram, Organs, Structures, and Functions
Kidney Embryology & Development: Easy Lesson
Psychology 101: Crowd Psychology and The Theory of Gustave Le Bon
Introduction to Evolution: Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace
Copyright © 2022 Moosmosis Organization: All Rights Reserved
All rights reserved. This essay first published on moosmosis.org or any portion thereof may not be reproduced or used in any manner whatsoever
without the express written permission of the publisher at moosmosis.org.

Please Like and Subscribe to our Email List at moosmosis.org, Facebook, Twitter, Youtube to support our open-access youth education initiatives! 🙂











![Heart Block: First Degree vs Second Degree (Type I and Type 2) vs Third Degree - ECG Findings, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis [MCAT, USMLE, Biology, Medicine]](https://moosmosis.files.wordpress.com/2023/04/heart_block.png?w=200&h=200&crop=1)

excellent article on direct hernia vs indirect hernia!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Seven! 🙂
LikeLike
You’re welcome Moosmosis!
LikeLike
you’re welcome!
LikeLike
Fascinating info on hernias
My uncle had an umbilical hernia and got surgery for it
LikeLiked by 2 people
Wishing your Uncle well wishes and speedy recovery!
LikeLike
Awesome essay on Indirect versus direct hernias!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you Alex! Very kind of you 🙂
LikeLike
This is helpful article on direct vs indirect hernias thank you
LikeLiked by 2 people
You’re very welcome! Glad to help 🙂
LikeLike
Direct hernias and indirect hernias are very common!
Especially the big hernias can certainly get in the way.
Surgery is in the books.
Excellent points about hernias!
LikeLiked by 1 person
Thank you, kind soul! You’re absolutely right. 🙂
LikeLike
So helpful!! Thanks!!
LikeLiked by 1 person
You’re very welcome Sara! 🙂 So glad to hear!!
LikeLike