Pushing Life’s Boundaries: Extremophiles Archaea
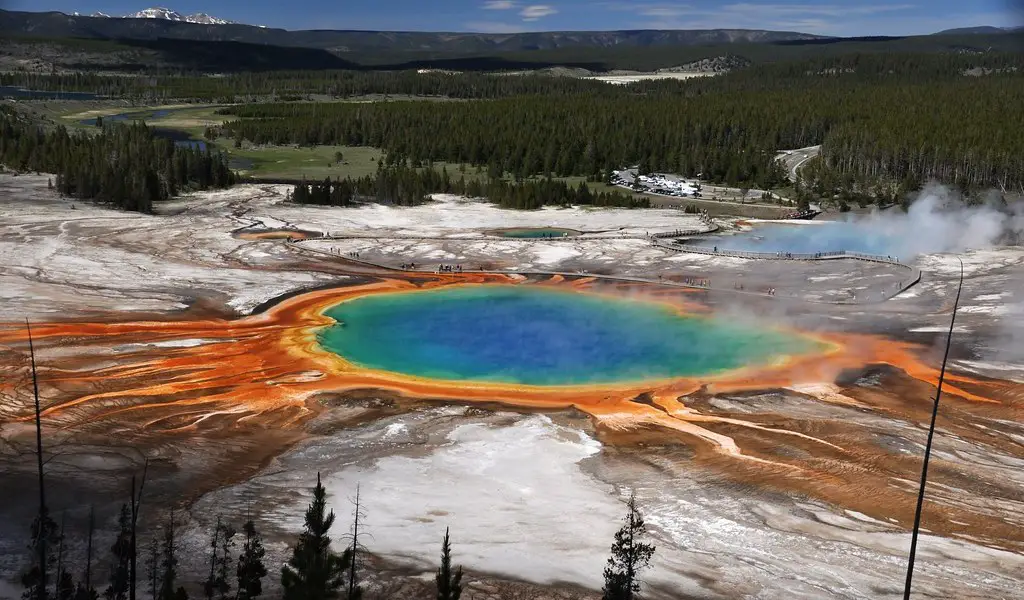
Moderate and extreme are relative terms. What many assume to be the normal conditions for life do not apply equally across all species. Habitability can be thought of in terms of the Goldilocks principle. For example, to survive people need an environment that is not too cold and not too hot. Ranges like this exist for other factors as well, such as pressure. However, what is just right for us and most other creatures can be too much or too little for some. Animals that live on the sea floor provide an illustrative example in this regard. Where people need submersibles to maintain their equilibria, creatures that natural selection has adapted to thrive in the ocean’s depths are right at home. Cold, highly pressurized environments are the norm for them. When deep sea creatures are brought to the surface through accident or scientific curiosity they often either melt, as with glacial ice worms, or fatally decompress, like with blobfish. In this way the term extremophile is a relative one and is used to describe organisms that live in environments that are extreme to us. Beyond their novelty, extremophiles are important objects of study as they challenge and expand our notions of life and its necessities.

























![Heart Block: First Degree vs Second Degree (Type I and Type 2) vs Third Degree - ECG Findings, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis [MCAT, USMLE, Biology, Medicine]](https://moosmosis.files.wordpress.com/2023/04/heart_block.png?w=200&h=200&crop=1)



